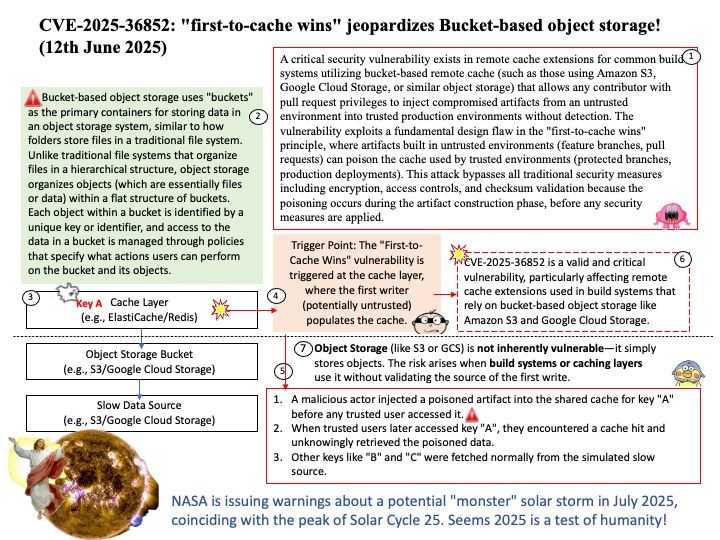
Preface: rfc3161-client version 1.0.3 is not designed to be installed on the server side. It’s a Python library, specifically a client-side tool, for interacting with RFC 3161 Time-Stamp Protocol (TSP) servers. It’s used to create timestamp requests and process timestamp responses, which is a client-side function of interacting with a time-stamping authority.
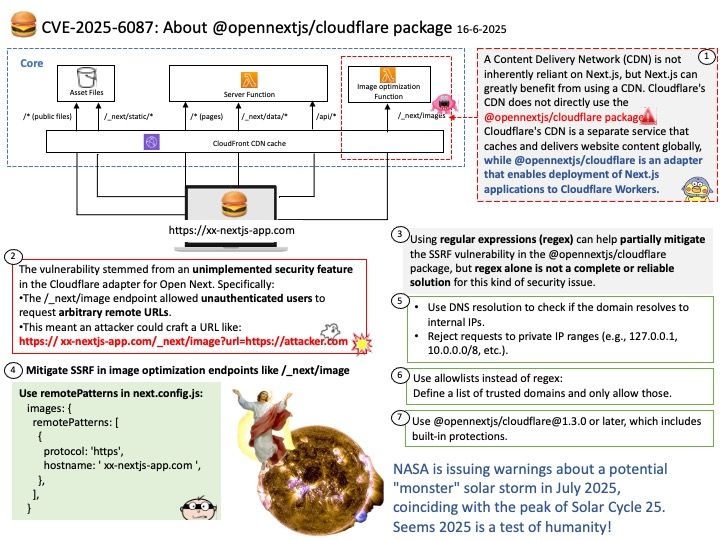
Background: The primary design objective of the Python Time-Stamp Protocol (TSP) library is to enable trusted timestamping of digital data. This means providing a secure and verifiable way to associate a specific point in time with electronic documents or signatures. The library allows users to request a timestamp token from a Time-Stamp Authority (TSA), which then attests to the existence of the data at that time.
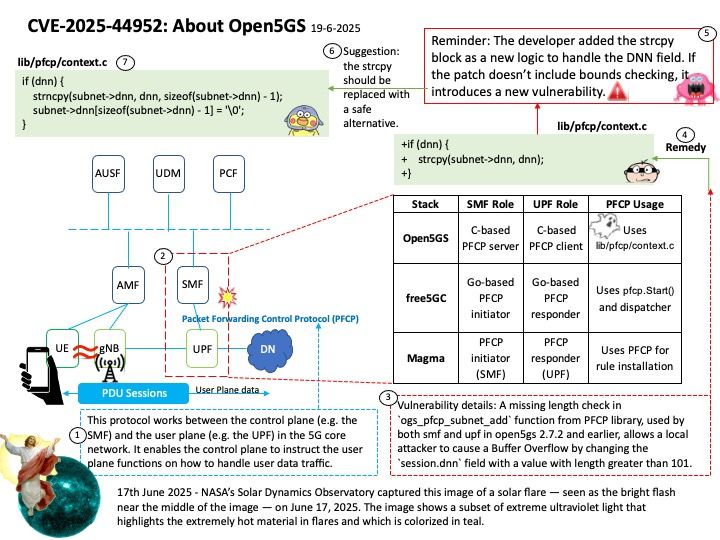
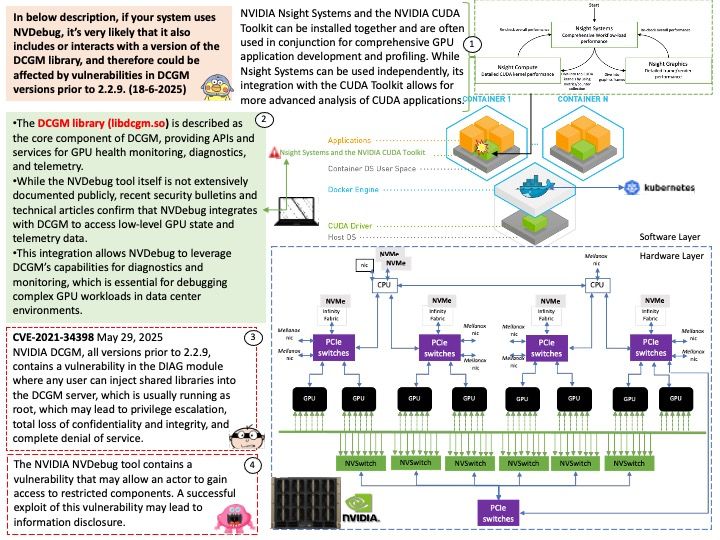
The Time-Stamp Protocol (TSP), defined in RFC 3161, is a cryptographic protocol used for trusted timestamping of electronic data. It involves a Time-Stamp Authority (TSA) that provides a digitally signed timestamp, proving that a specific piece of data existed before a certain point in time. This is achieved by hashing the data, sending the hash to the TSA, and receiving a timestamp token containing the hash, a unique serial number, a timestamp, and the TSA’s digital signature.
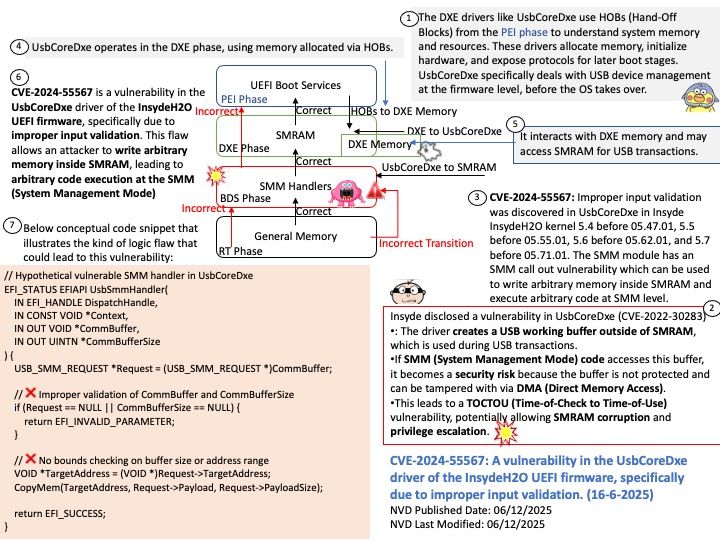
Ref: TSR (Trust Store Repository) embedded certificates up to the trusted root(s) form the foundation of a chain of trust, allowing devices and systems to verify the authenticity and trustworthiness of other certificates. These embedded certificates, often root certificates, act as the ultimate authority, establishing a baseline for trust within the system.
Vulnerability details: rfc3161-client is a Python library implementing the Time-Stamp Protocol (TSP) described in RFC 3161. Prior to version 1.0.3, there is a flaw in the timestamp response signature verification logic. In particular, chain verification is performed against the TSR’s embedded certificates up to the trusted root(s), but fails to verify the TSR’s own signature against the timestamping leaf certificates. Consequently, vulnerable versions perform insufficient signature validation to properly consider a TSR verified, as the attacker can introduce any TSR signature so long as the embedded leaf chains up to some root TSA.
Official announcement: For details, please see the reference website – https://nvd.nist.gov/vuln/detail/CVE-2025-52556