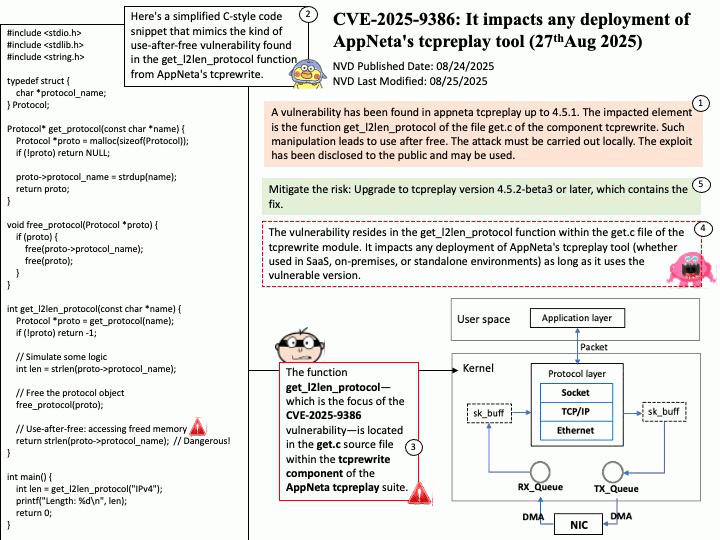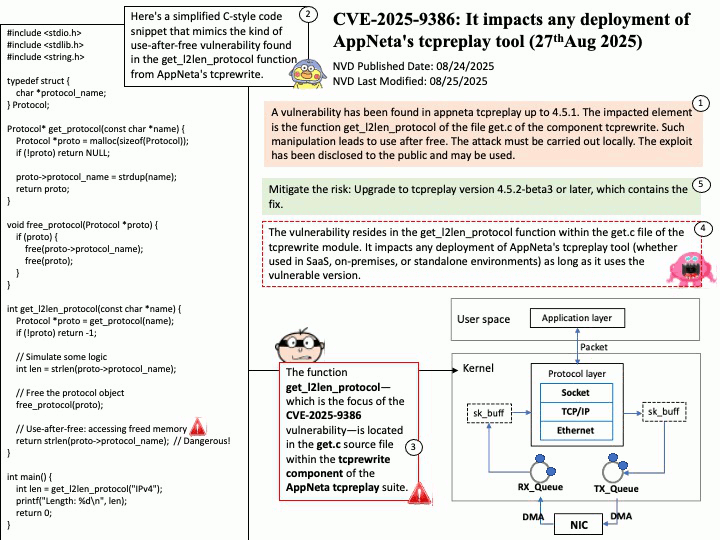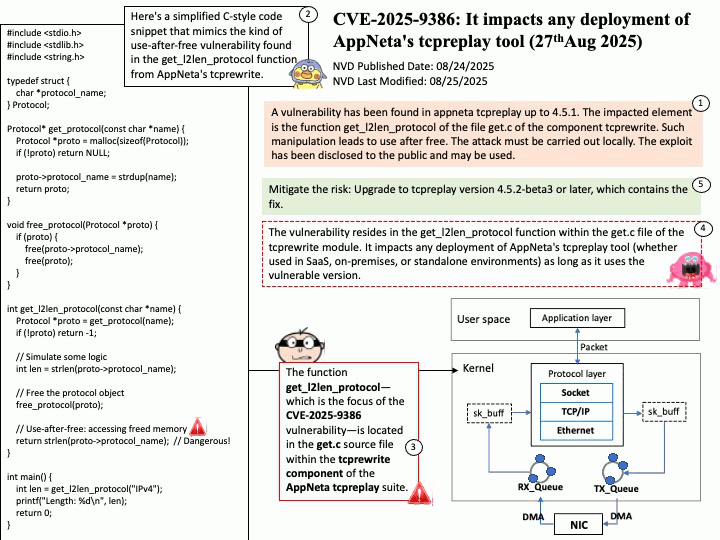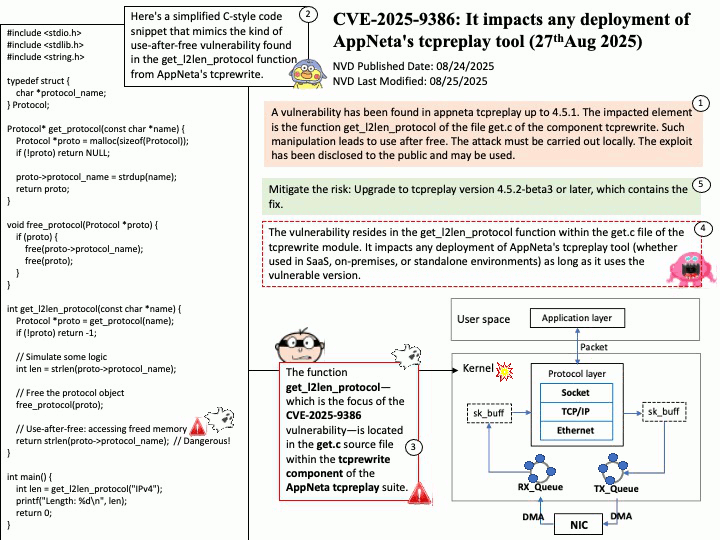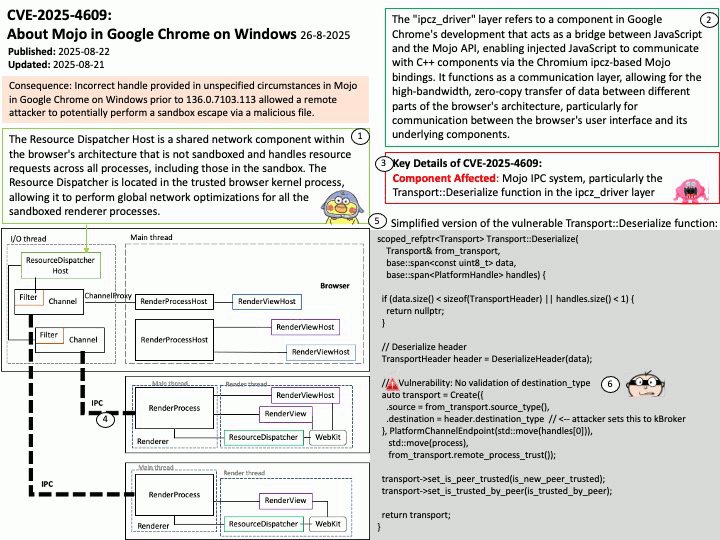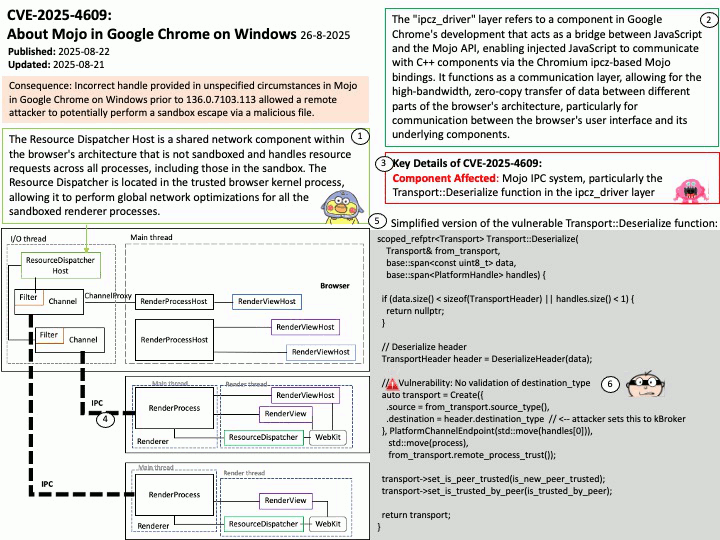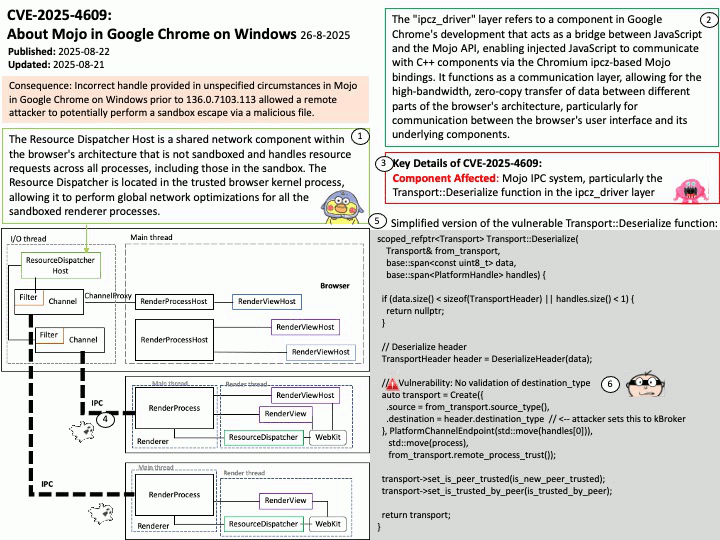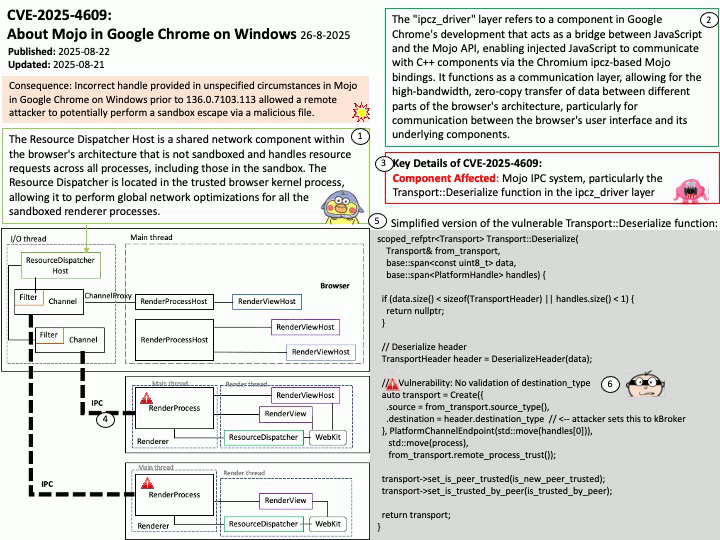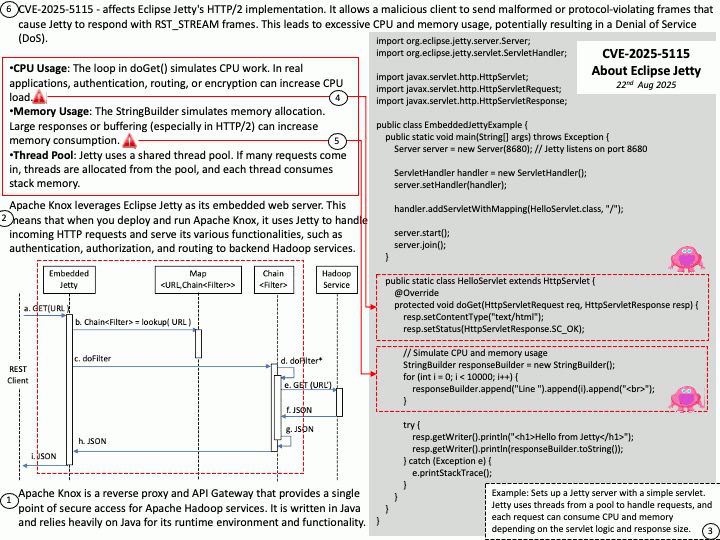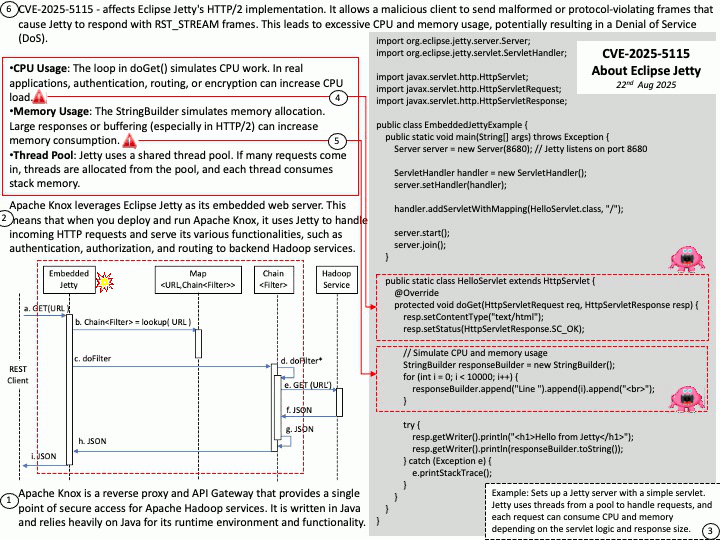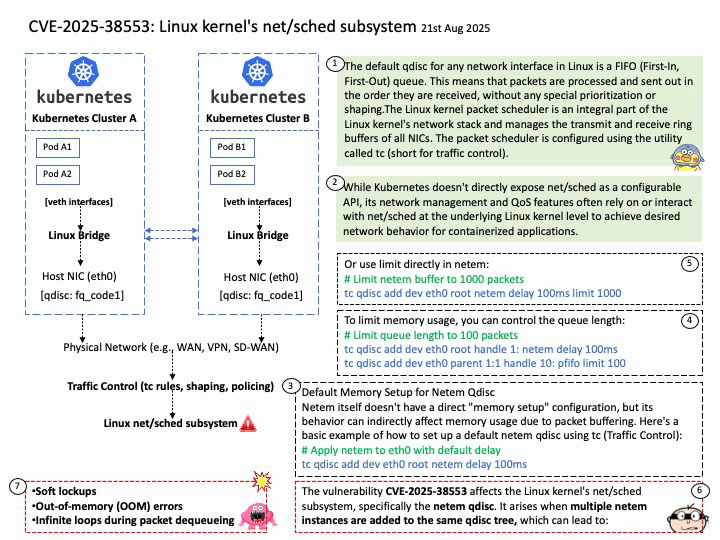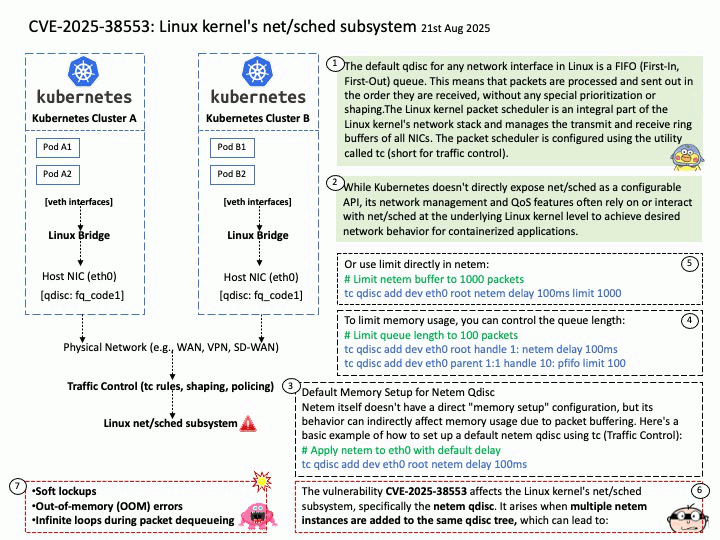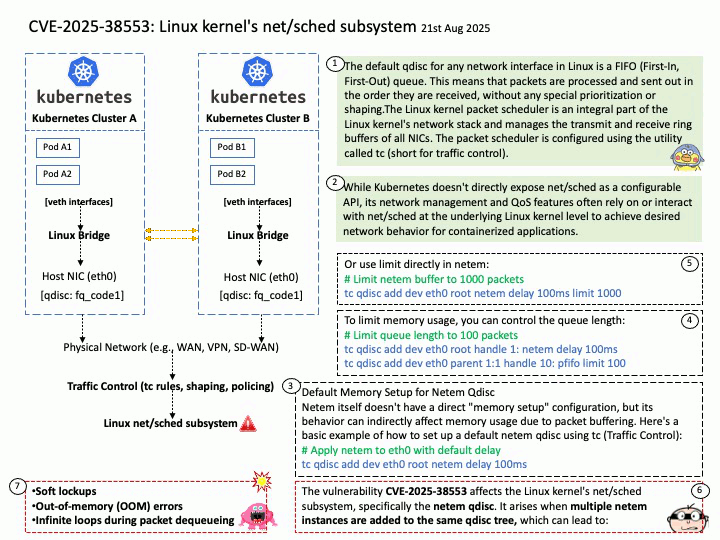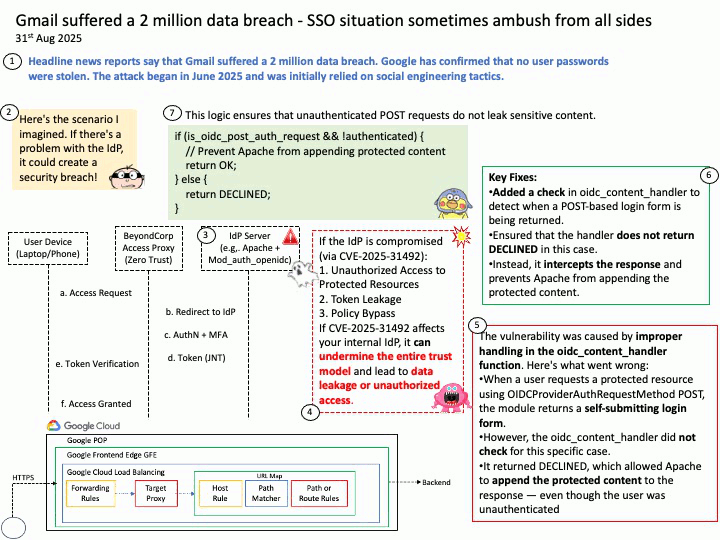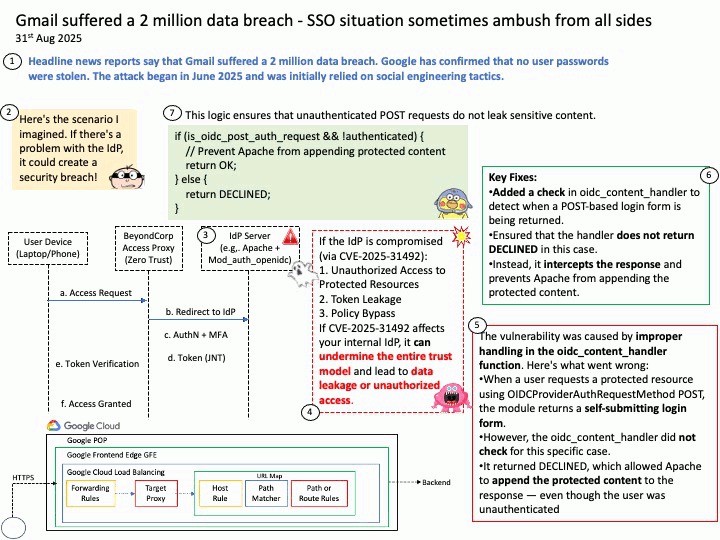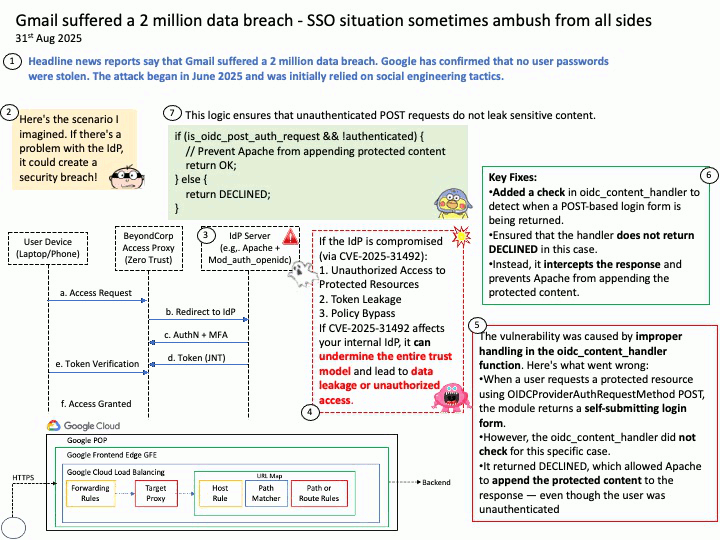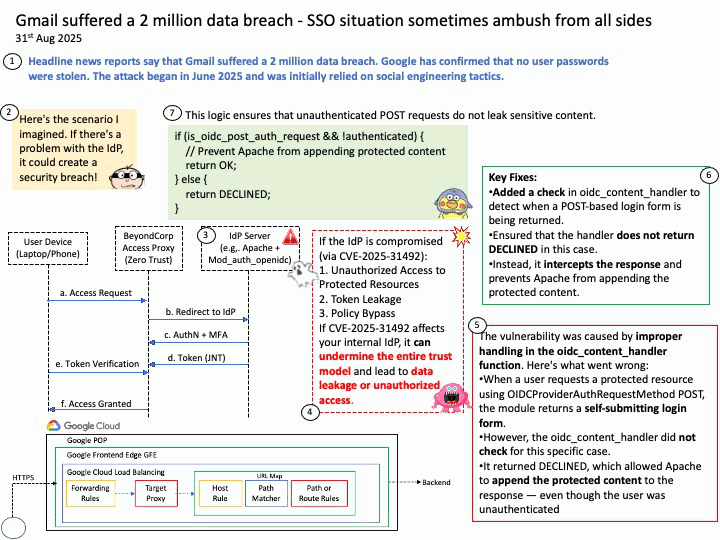
Quote: Google warns 2.5B Gmail users to update passwords after data breach of one of its databases – https://nypost.com/2025/08/27/business/google-warns-2-5-billion-gmail-users-to-update-passwords-after-hackers-complete-successful-intrusions/
Preface: More than 2.5 billion Gmail users could be at risk following a massive cyberattack that compromised a Google database managed through Salesforce’s cloud platform. The attack, which began in June 2025, relied on social engineering tactics. According to Google’s Threat Intelligence Group (GTIG), scammers impersonated IT staff during convincing phone calls and persuaded a Google employee to approve a malicious application connected to Salesforce. This gave attackers the ability to exfiltrate contact details, business names, and related notes. (Source: Trend Micro) – https://news.trendmicro.com/2025/08/26/google-data-breach-gmail/
Background: BeyondCorp® is a cybersecurity architecture developed at Google that shifts access control from the traditional network perimeter to individual devices and users. The goal is to enable users to securely work anytime, anywhere and on any device without having to use a virtual private network, or VPN, to access an organization’s resources.
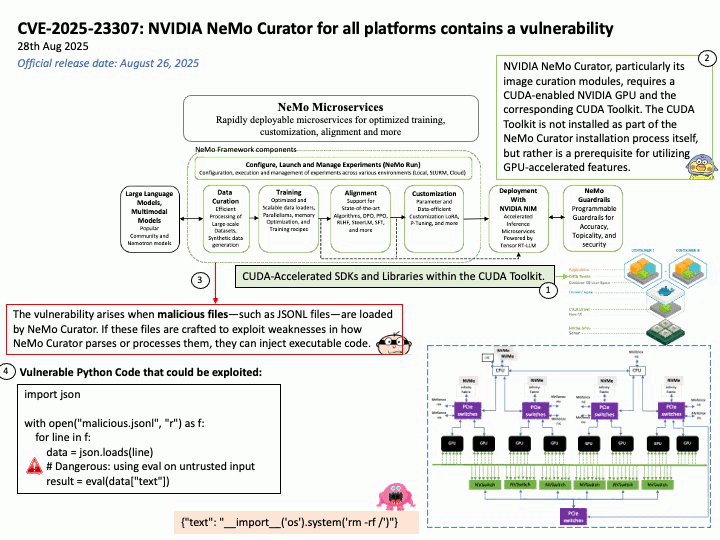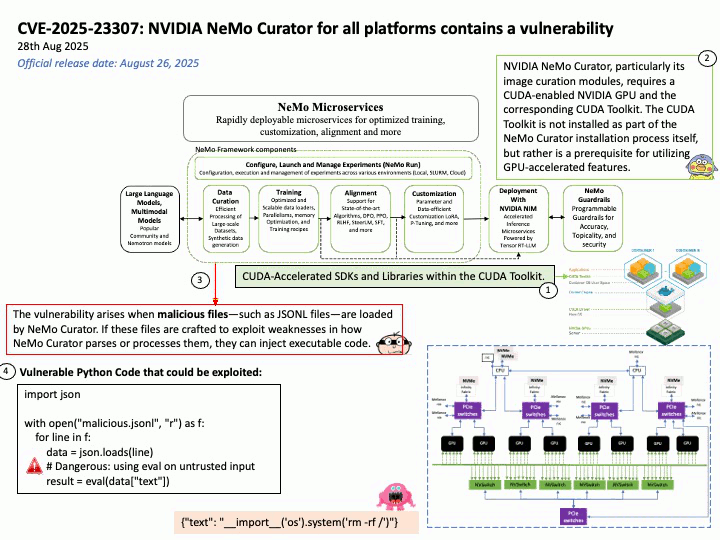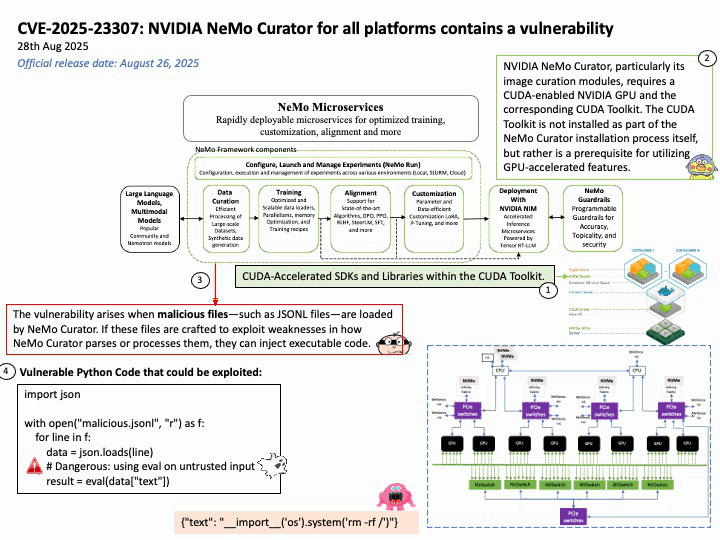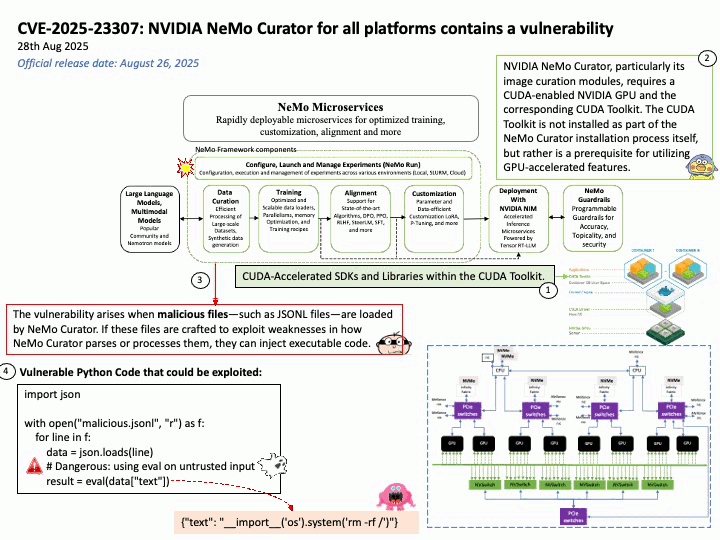
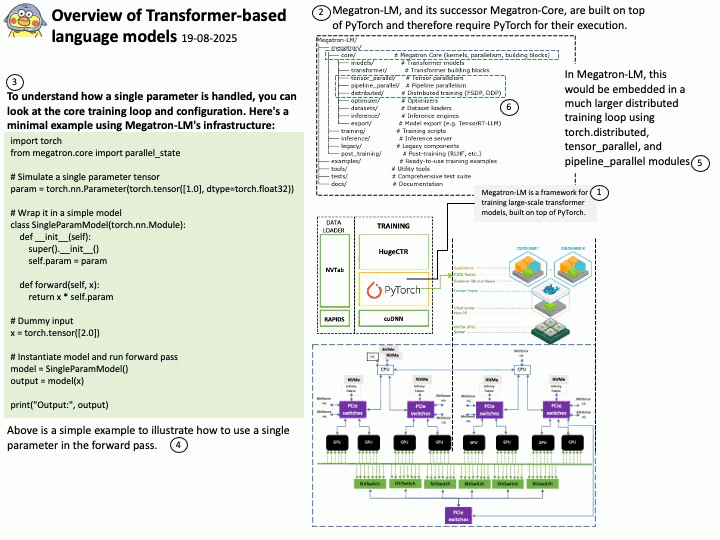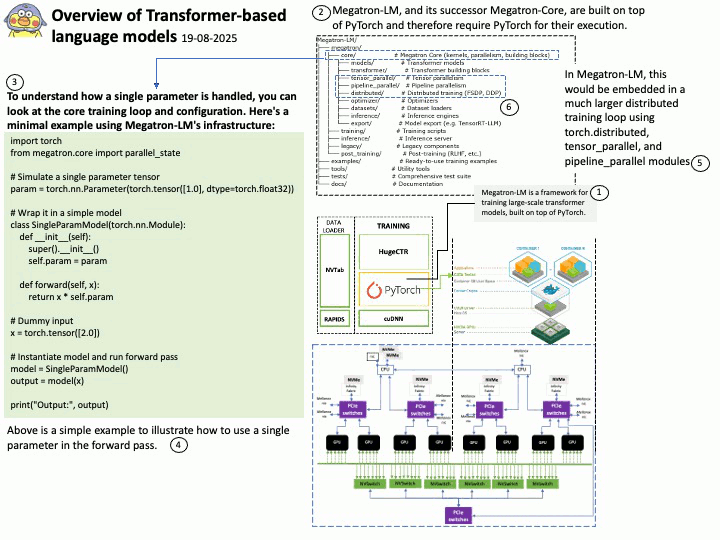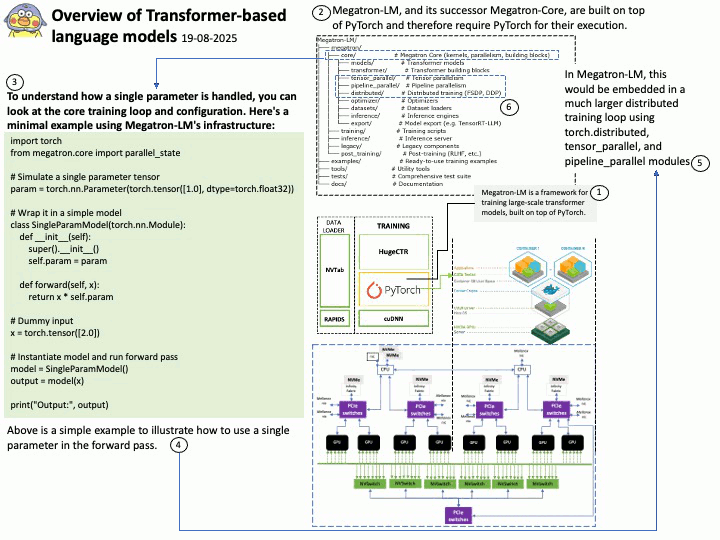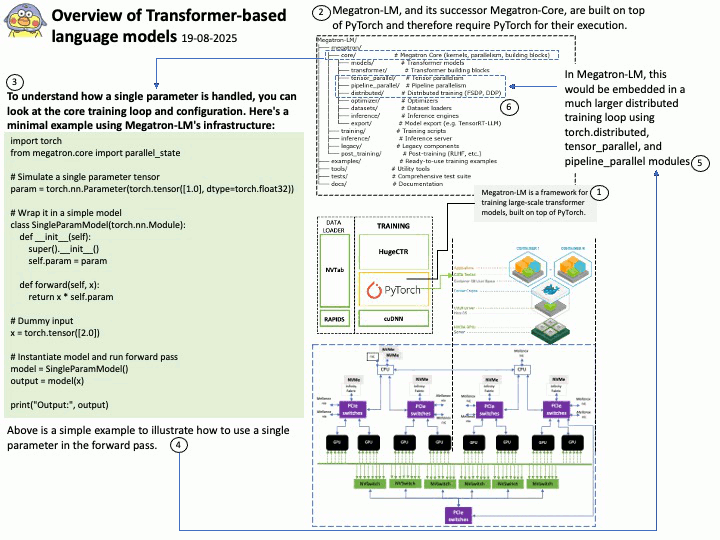
Google uses OpenID Connect (OIDC) for its “Sign in with Google” functionality, as it is an OpenID Connect Provider that issues OIDC-formatted JSON Web Tokens (JWTs) to authenticate users and share identity information with client applications. This allows users to log into other websites and applications using their Google account, benefiting from a simplified and more secure single sign-on (SSO) experience.
OAuth 2.0 is an authorization framework, OpenID Connect (OIDC) is an identity layer built on top of OAuth 2.0 to provide user authentication and identity information. OAuth 2.0 focuses on granting access to protected resources, while OIDC extends it to verify a user’s identity and share their profile information with third-party applications.
About the title: Please see the attached diagram.
Ref: Gmail utilizes a protocol called OpenID Connect (OIDC) for authentication, which is built on top of the OAuth 2.0 authorization framework. This protocol allows users to log in to various applications by authenticating with their Google Account without sharing their passwords directly, enabling both authentication (verifying identity) and authorization (granting access to specific data). For Gmail access, OAuth 2.0 is used for authorization, while OIDC provides the user authentication mechanism, returning an ID Token in addition to an access token for identity verification.