Preface: The IPv4-mapped IPv6 address format allows the IPv4 address of an IPv4 node to be represented as an IPv6 address. The IPv4 address is encoded into the low-order 32 bits of the IPv6 address, and the high-order 96 bits hold the fixed prefix 0:0:0:0:0:FFFF.
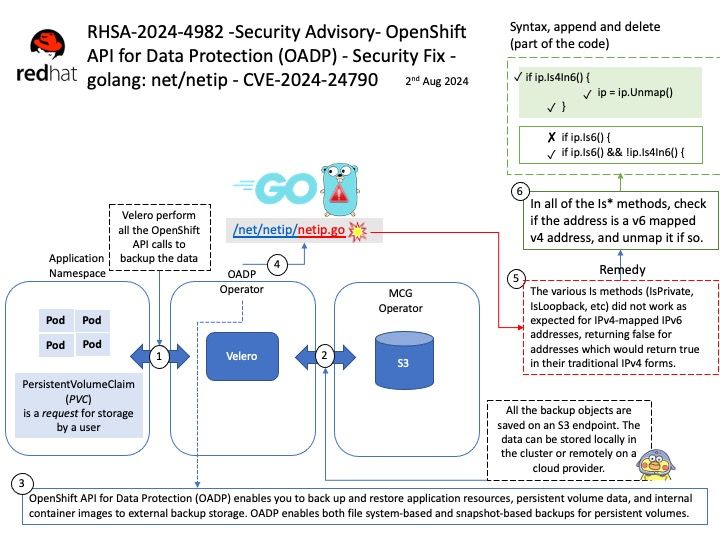
Background: OpenShift API for Data Protection (OADP) enables you to back up and restore application resources, persistent volume data, and internal container images to external backup storage. OADP enables both file system-based and snapshot-based backups for persistent volumes.
Package netip defines an IP address type that’s a small value type. Building on that Addr type, the package also defines AddrPort (an IP address and a port) and Prefix (an IP address and a bit length prefix).
Compared to the net.IP type, Addr type takes less memory, is immutable, and is comparable (supports == and being a map key).
Vulnerability details: OpenShift API for Data Protection (OADP) enables you to back up and restore application resources, persistent volume data, and internal container images to external backup storage. OADP enables both file system-based and snapshot-based backups for persistent volumes.
Security Fixes from Bugzilla: golang: net/netip: Unexpected behavior from Is methods for IPv4-mapped IPv6 addresses (CVE-2024-24790)
Official announcement: Please refer to the website for details – https://access.redhat.com/errata/RHSA-2024:4982