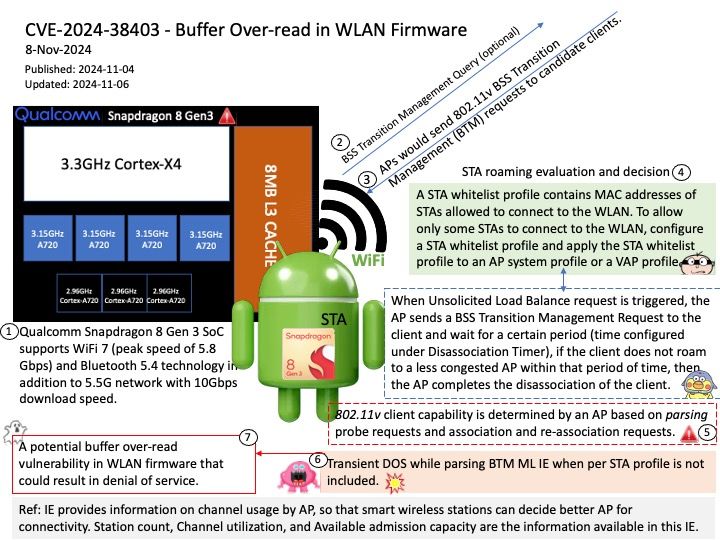
Preface: The Cortex-M3 processor is specifically developed for high-performance, low-cost platforms for a broad range of devices including microcontrollers, automotive body systems, industrial control systems and wireless networking and sensors.
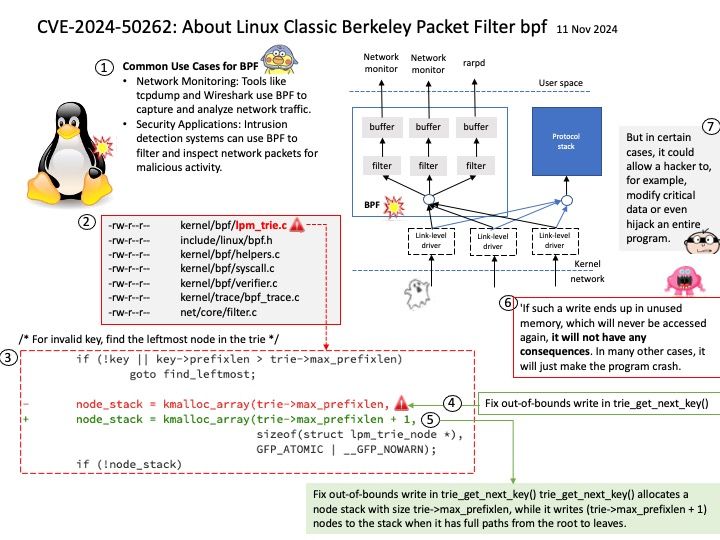
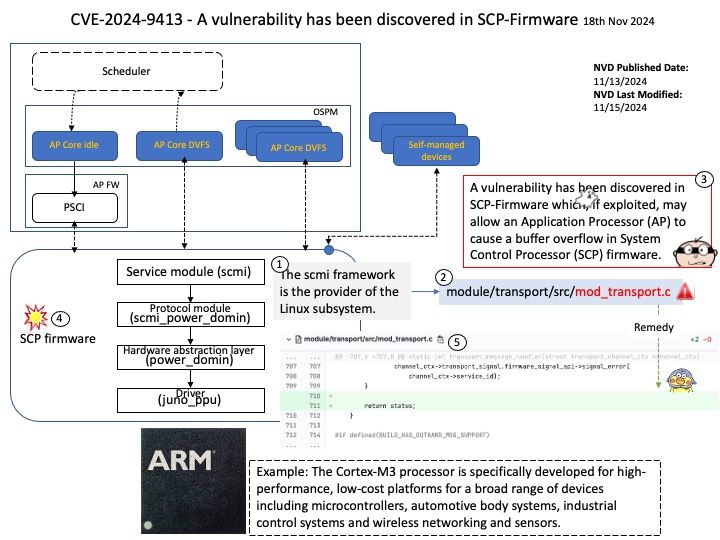
Background: SCP Firmware provides a software reference implementation for the System Control Processor (SCP) and Manageability Control Processor (MCP) components found in several Arm Compute Sub-Systems. Functionality.
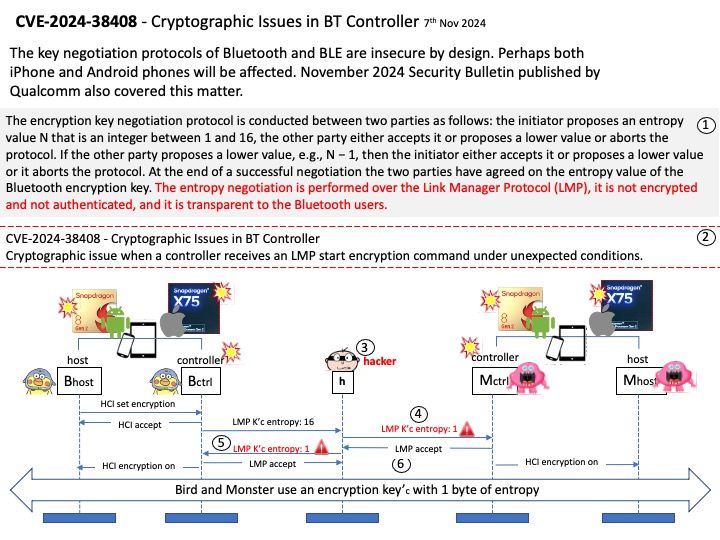
Description. Initialization. Initialization of the system to enable application core boot.
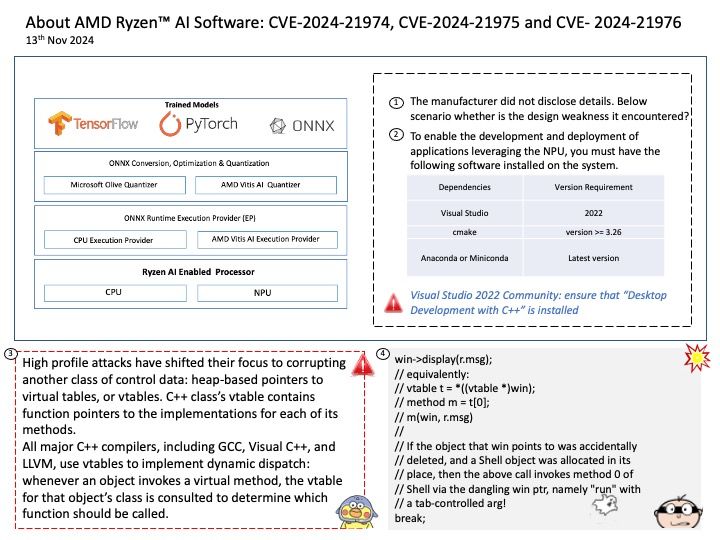
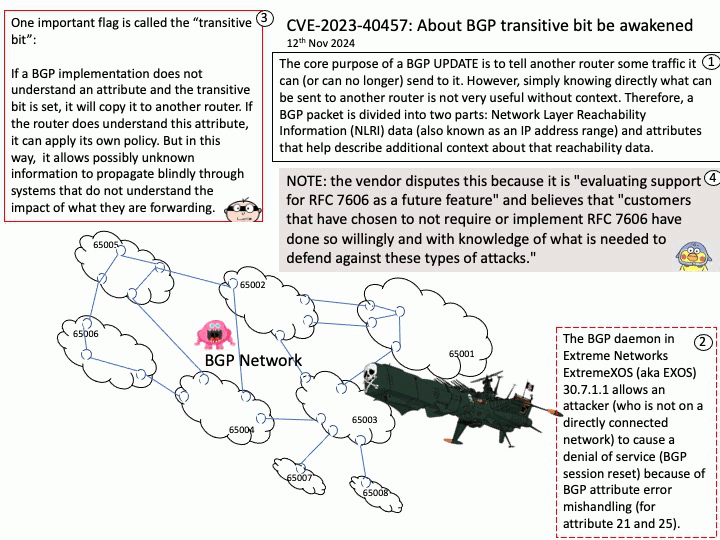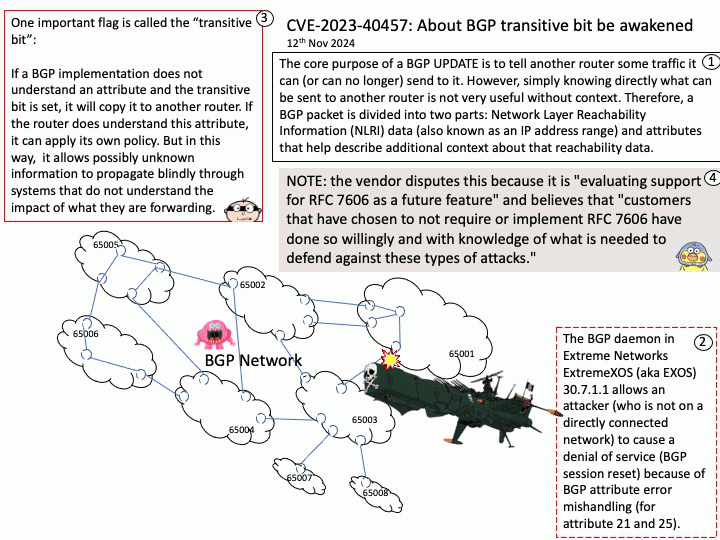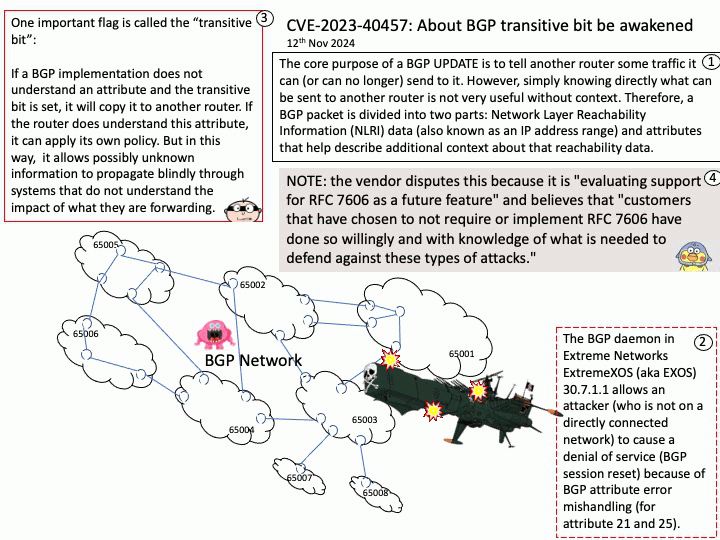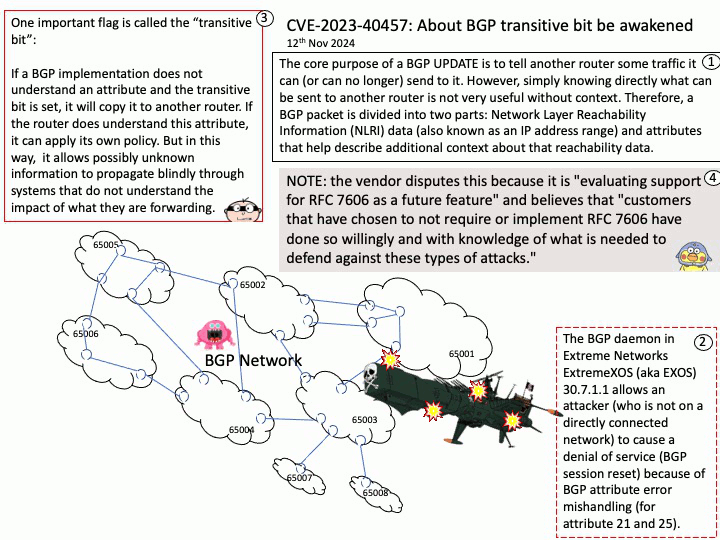
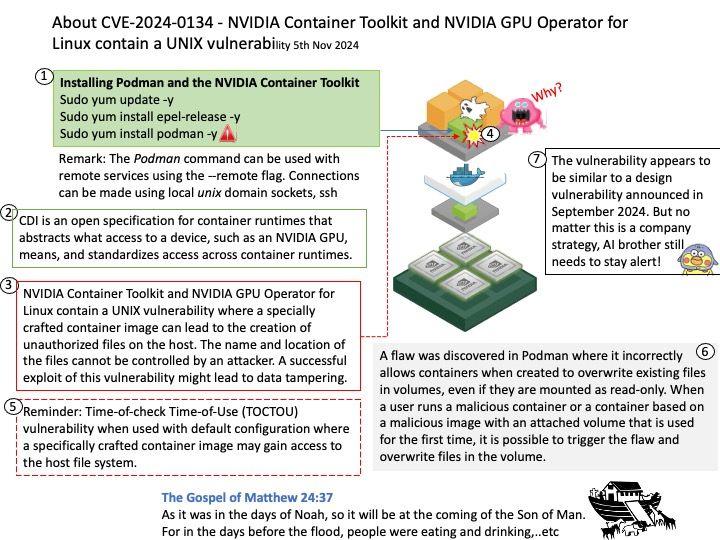
Power Control System Architecture (PCSA) defines the concept of a System Control Processor (SCP), a specialized processor that abstracts power and system management tasks from the application processor.
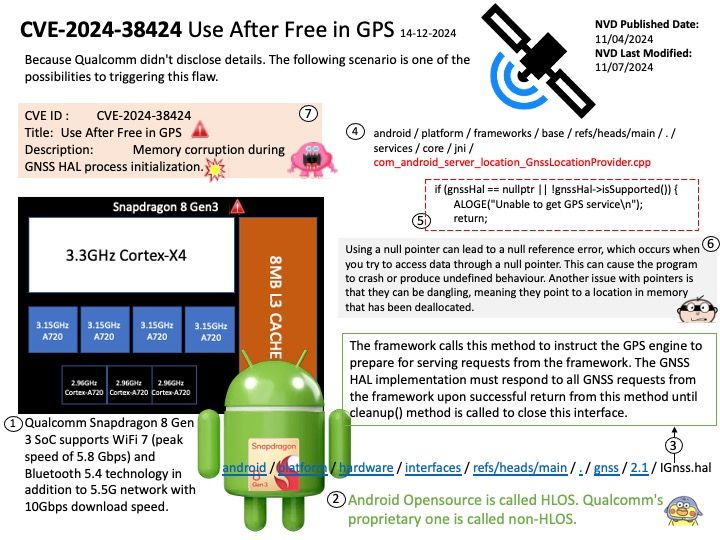
Vulnerability details: The transport_message_handler function in SCP-Firmware release versions 2.11.0-2.15.0 does not properly handle errors, potentially allowing an Application Processor (AP) to cause a buffer overflow in System Control Processor (SCP) firmware.
Official announcement: For detail, please refer to link –