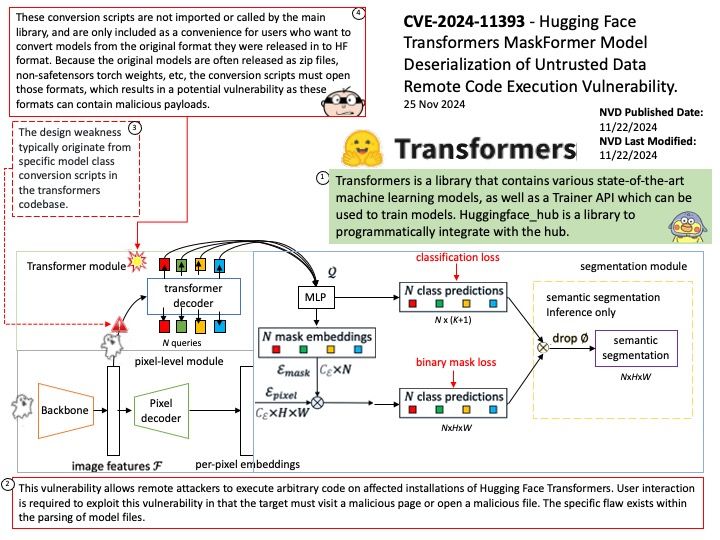
Preface: Preface: Imagination Technologies Group Limited is a British semiconductor and software design company owned by Canyon Bridge Capital Partners, a private equity fund based in Beijing that is ultimately owned by the Chinese government. With its global headquarters in Kings Langley, England, its primary business is in the design of PowerVR mobile graphics processors (GPUs), neural network accelerators for AI processing, and networking routers. The company was listed on the London Stock Exchange until it was acquired by Canyon Bridge in November 2017.
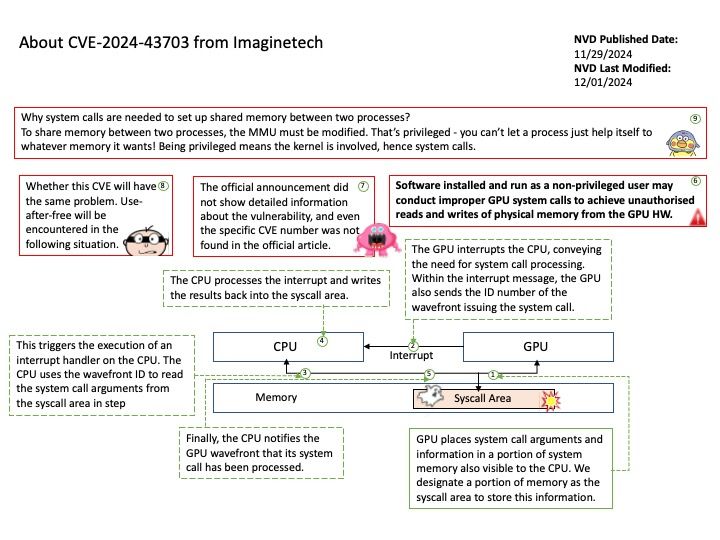
Background: Why system calls are needed to set up shared memory between two processes?
To share memory between two processes, the MMU must be modified. That’s privileged – you can’t let a process just help itself to whatever memory it wants! Being privileged means the kernel is involved, hence system calls.
Remark: A memory management unit (MMU), sometimes called paged memory management unit (PMMU), is a computer hardware unit that examines all memory references on the memory bus, translating these requests, known as virtual memory addresses, into physical addresses in main memory.
Vulnerability details: Software installed and run as a non-privileged user may conduct improper GPU system calls to achieve unauthorised reads and writes of physical memory from the GPU HW.
Official announcement: Please see the link below for details –