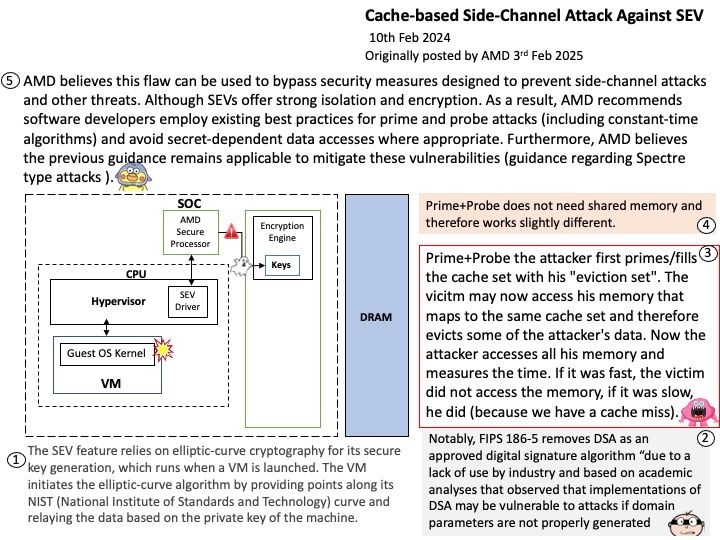
Released on February 18, 2025
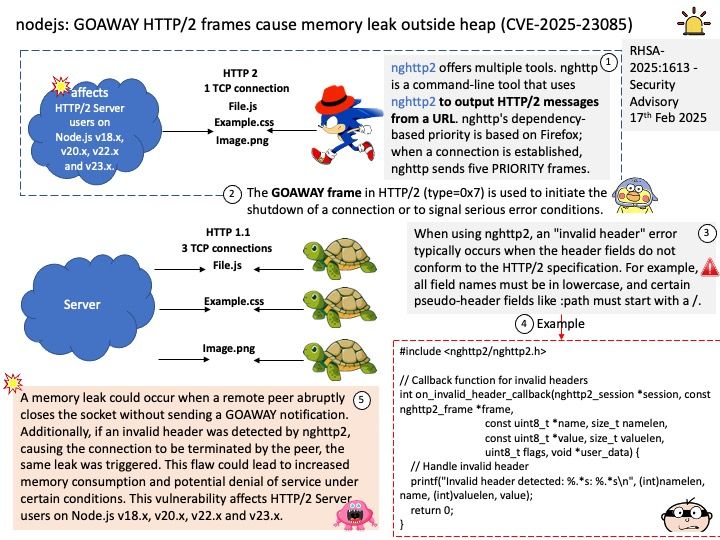
Preface: In NVIDIA CUDA, cuobjdump and nvdisasm are two binary utilities used for examining and disassembling CUDA binaries (cubin files).
cuobjdump
- Purpose: It can disassemble CUDA binaries and extract PTX (Parallel Thread Execution) code from host binaries, executables, object files, static libraries, and external fatbinary files.
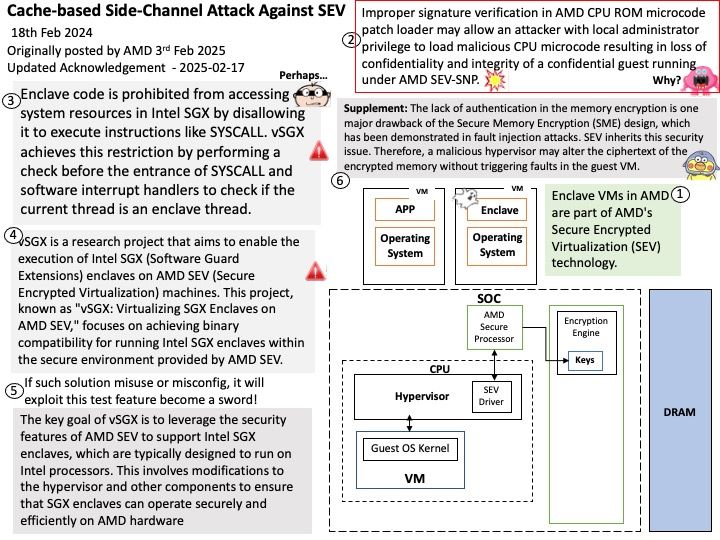
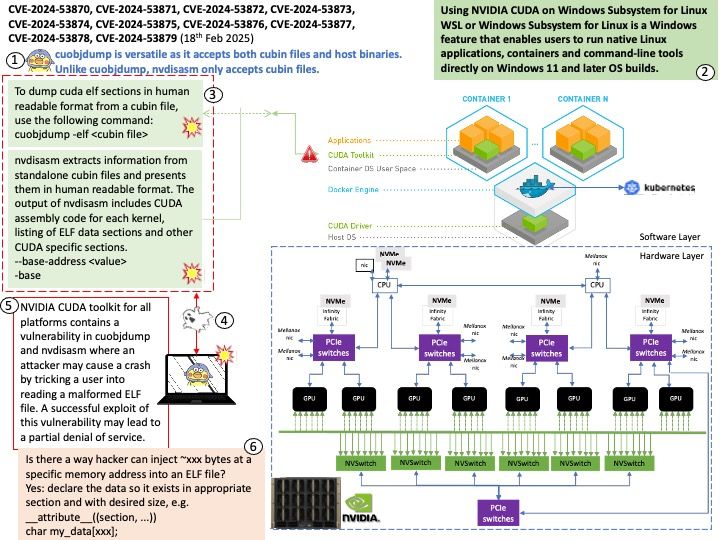
- Usage: cuobjdump is versatile as it accepts both cubin files and host binaries.
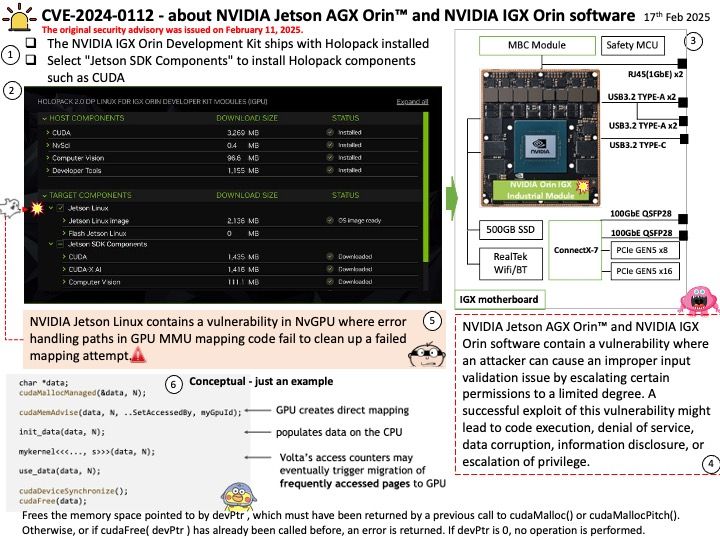
- Features: It provides basic disassembly and extraction capabilities but lacks advanced display options and control flow analysis.
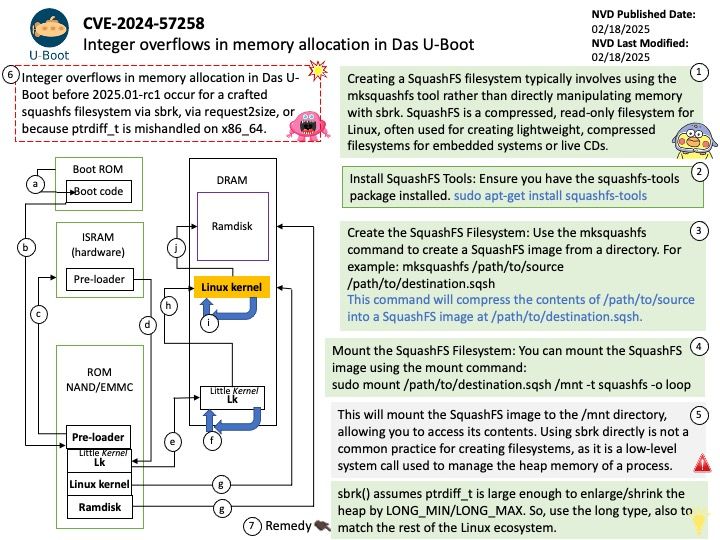
nvdisasm
- Purpose: It is specifically designed to disassemble cubin files.
- Usage: Unlike cuobjdump, nvdisasm only accepts cubin files.
- Features: It offers richer output options, including advanced display options and control flow analysis.
These tools are essential for developers who need to inspect and debug the compiled CUDA code.
Background: Parallel processing is a method in computing of running two or more processors (CPUs) to handle separate parts of an overall task. Breaking up different parts of a task among multiple processors will help reduce the amount of time to run a program. GPUs render images more quickly than a CPU because of its parallel processing architecture, which allows it to perform multiple calculations across streams of data simultaneously. The CPU is the brain of the operation, responsible for giving instructions to the rest of the system, including the GPU(s).
NVIDIA CUDA provides a simple C/C++ based interface. The CUDA compiler leverages parallelism built into the CUDA programming model as it compiles your program into code.
CUDA is a parallel computing platform and programming interface model created by Nvidia for the development of software which is used by parallel processors. It serves as an alternative to running simulations on traditional CPUs.
Vulnerability details:
The following two design flaws are associated with these CVEs:
CVE‑2024‑53870, CVE‑2024‑53871, CVE‑2024‑53872, CVE‑2024‑53873, CVE‑2024‑53874, CVE‑2024‑53875, CVE‑2024‑53876, CVE‑2024‑53877, CVE‑2024‑53878 and CVE‑2024‑53879
NVIDIA CUDA toolkit for Linux and Windows contains a vulnerability in the cuobjdump binary, where a user could cause a crash by passing a malformed ELF file to cuobjdump. A successful exploit of this vulnerability might lead to a partial denial of service.
NVIDIA CUDA toolkit for all platforms contains a vulnerability in the nvdisasm binary, where a user could cause an out-of-bounds read by passing a malformed ELF file to nvdisasm. A successful exploit of this vulnerability might lead to a partial denial of service.
Official announcement: Please refer to the vendor announcement for details – https://nvidia.custhelp.com/app/answers/detail/a_id/5594