Preface: SSH clients are designed for direct user interaction, providing a command-line interface (CLI) or graphical user interface (GUI) on the initiating device. The SSHD operates as a background process, running silently in the background without any user intervention.
Background: How do I make my SSH connection more stable?
SSH servers often have an idle timeout period, after which they automatically disconnect idle sessions. To prevent premature disconnections, consider modifying the server’s idle timeout setting. To modify the idle timeout: Locate the SSH server configuration file, typically located at /etc/ssh/sshd_config .
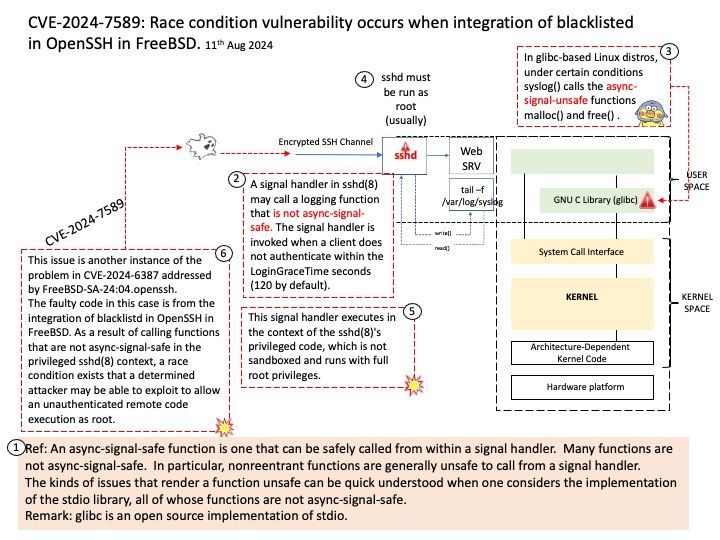
Vulnerability details: A signal handler in sshd(8) may call a logging function that is not async-signal-safe. The signal handler is invoked when a client does not authenticate within the LoginGraceTime seconds (120 by default). This signal handler executes in the context of the sshd(8)’s privileged code, which is not sandboxed and runs with full root privileges. This issue is another instance of the problem in CVE-2024-6387 addressed by FreeBSD-SA-24:04.openssh.
The faulty code in this case is from the integration of blacklistd in OpenSSH in FreeBSD. As a result of calling functions that are not async-signal-safe in the privileged sshd(8) context, a race condition exists that a determined attacker may be able to exploit to allow an unauthenticated remote code execution as root.
Official announcement: Please refer to the link for details https://www.tenable.com/cve/CVE-2024-7589