Preface: Libxml2, a C library for parsing and manipulating XML documents, can be relevant in machine learning contexts when dealing with data stored or exchanged in XML format. While not a machine learning library itself, libxml2, or its Python binding lxml, serves as a foundational tool for data preparation and feature engineering.
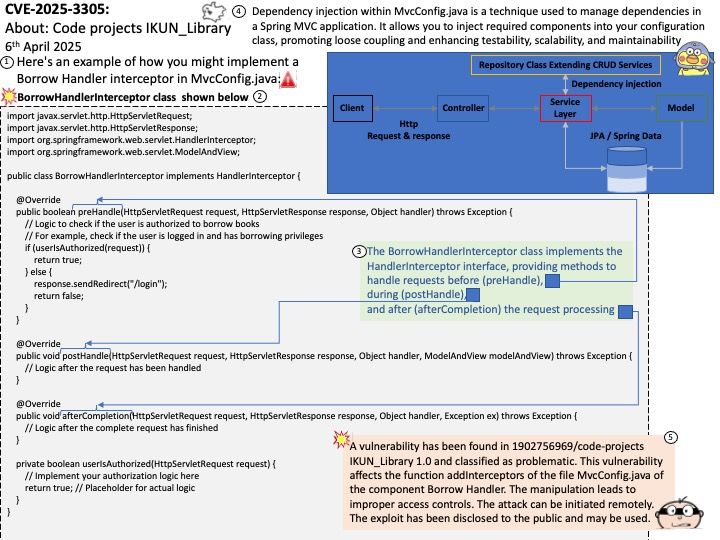
Ref: The “difference” between Libxml and Libxml2 is that they are essentially the same thing, with “libxml2” being the official and specific name for the library.
Background: Moving nodes between XML documents can happen in machine learning workflows, especially during data integration, comparison, or transformation.
When would you be at risk?
You’d be at risk if:
- You use
libxml2orlxmlto move nodes from one document to another (e.g., merging XML trees). - The underlying library internally calls
xmlSetTreeDoc()during such operations. - The original document gets freed while namespace pointers still reference it.
Vulnerability details: A flaw was found in the xmlSetTreeDoc() function of the libxml2 XML parsing library. This function is responsible for updating document pointers when XML nodes are moved between documents. Due to improper handling of namespace references, a namespace pointer may remain linked to a freed memory region when the original document is destroyed. As a result, subsequent operations that access the namespace can lead to a use-after-free condition, causing an application crash.
Official announcement: Please refer to the link for details.