Preface: If you talk to God, what is the difference between human and artificial intelligence? Maybe God will say that humans and A.I are incomparable. And both cannot live together in the same place.
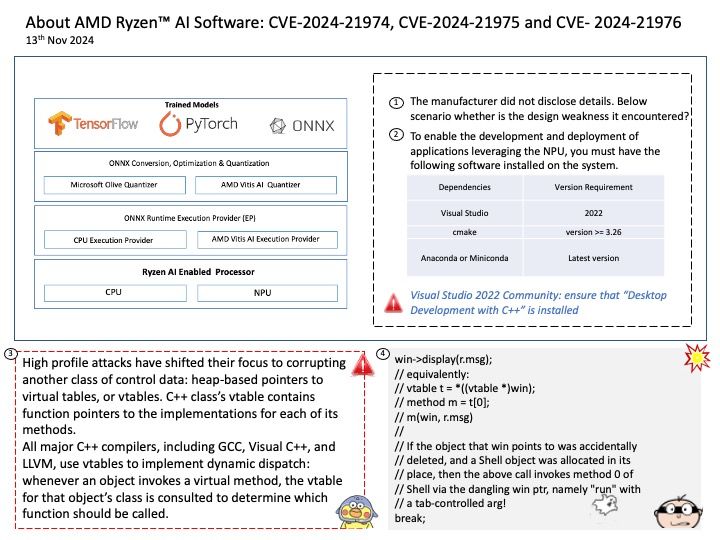
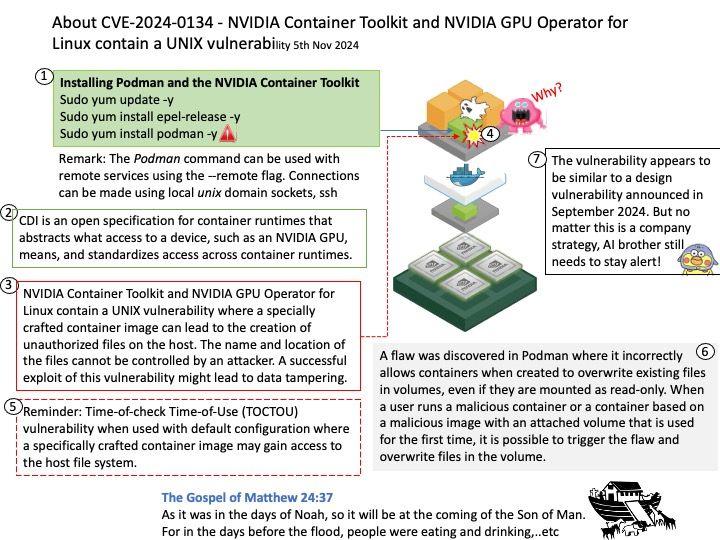
Background: Intel Neural Compressor performs model optimization to reduce the model size and increase the speed of deep learning inference for deployment on CPUs or GPUs.
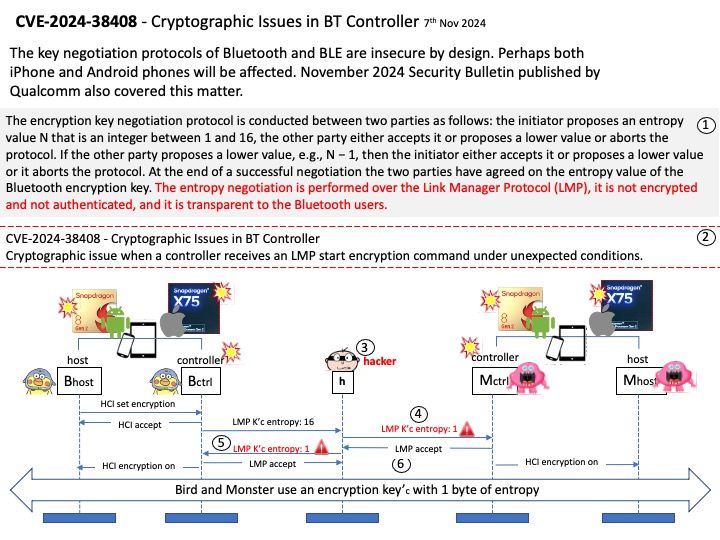
Intel Neural Compressor aims to provide popular model compression techniques such as quantization, pruning (sparsity), distillation, and neural architecture search on mainstream frameworks such as TensorFlow, PyTorch, ONNX Runtime, and MXNet, as well as Intel extensions such as Intel Extension for TensorFlow and Intel Extension for PyTorch.
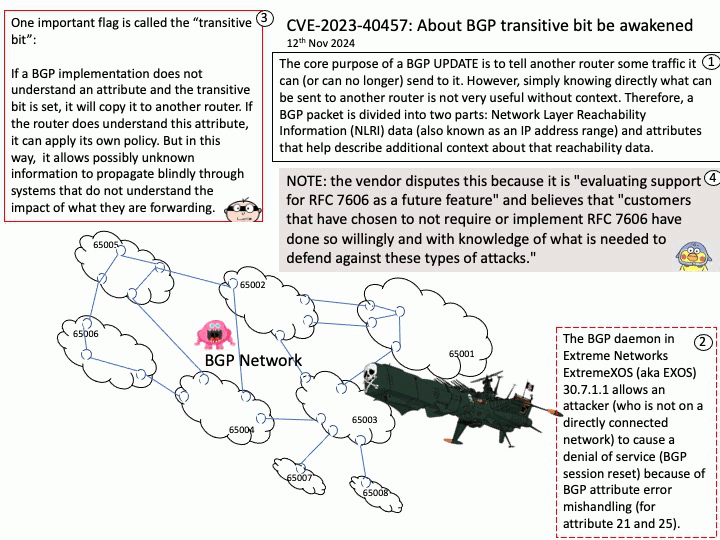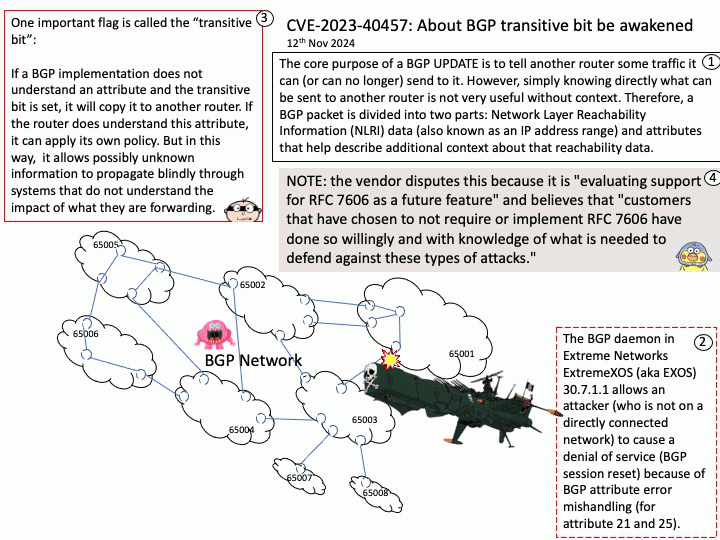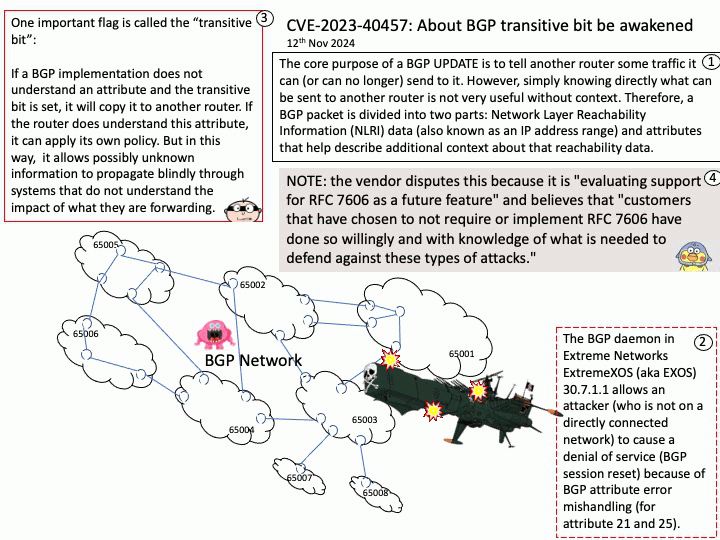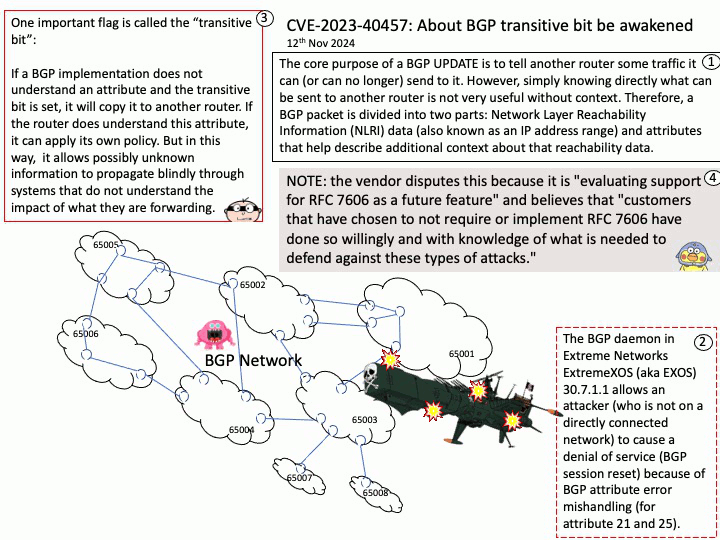
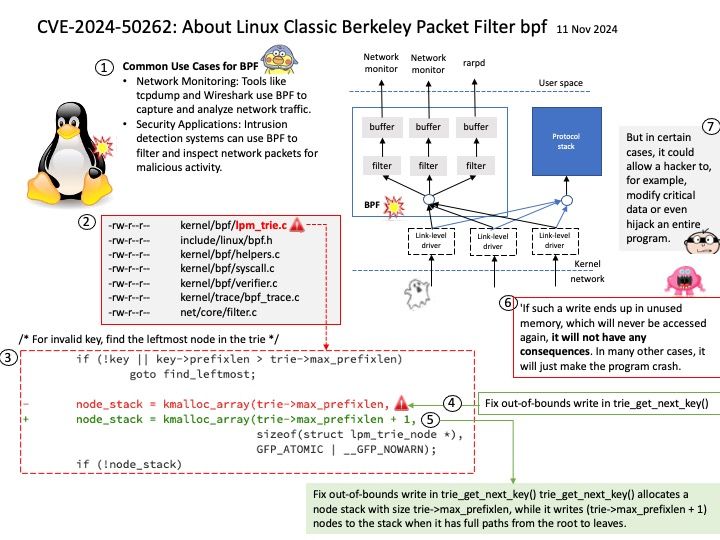
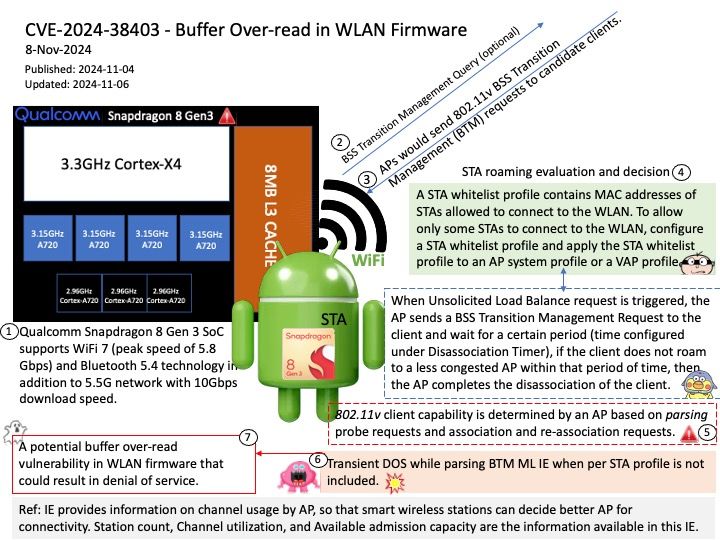
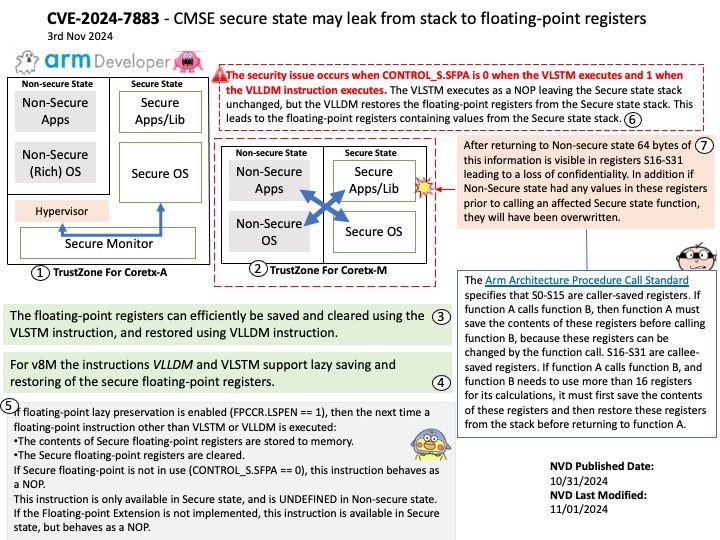
Vulnerability details:
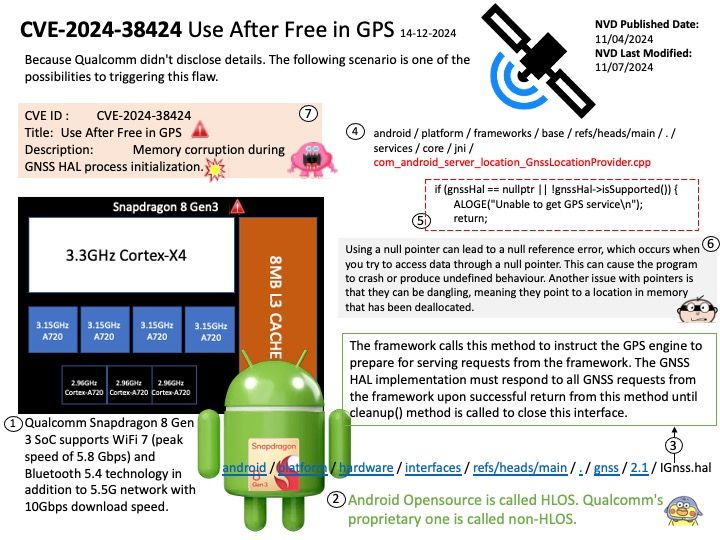
CVEID: CVE-2024-28028
Improper input validation in some Intel(R) Neural Compressor software before version v3.0 may allow an unauthenticated user to potentially enable escalation of privilege via adjacent access.
Affected Products: Intel® Neural Compressor software before version 3.0.
Official announcement: For detail, please refer to link – https://nvd.nist.gov/vuln/detail/CVE-2024-28028